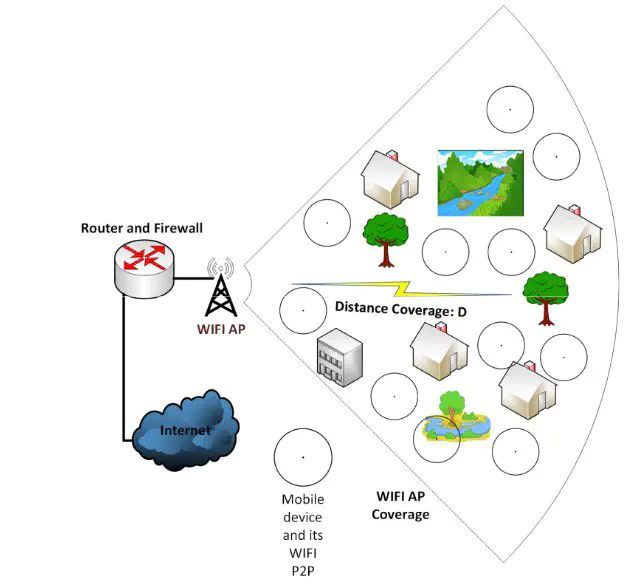
 A scenario case study schema
A scenario case study schemaAbstract
Recently, humans are more and more dependent to communication technologies (CT) in their everyday life to get services, exchange information and communicate with their relatives. Hence, many researches have been made in order to propose convenient and low-cost solutions compatible with the context of smart spaces. This paper characterizes the range of WiFi for outdoor applications in comparison with most known empirical path loss models, and analyzes its impact for smart space services like Internet of Things (IoT). The obtained range is 550m tested with a Samsung Galaxy S5 smartphone, and the comparison with empirical model showed a good difference. Hence the validity and accuracy of those models will be examined for this context, in order to develop an empirical model taking into account environmental effect during our future research. As solutions based on WiFi are generally low cost, its technical characteristics are illustrated and a wide deployment scenario based on this technology is explained on light of obtained results.